Inbound HTTPS component
The Inbound HTTPS component can receive messages through HTTPS requests. It acts like a web service that 'listens' for incoming requests. Once a message is received, it's content is handed over to the next component in the flow.
Configuration
The Inbound HTTPS component has the following configuration options:
Endpoint
A name to identify this component's endpoint (URL). By default, the option 'Set flow name as endpoint' is enabled. Disabling this option reveals a textbox where you can define the endpoint name manually.
The URL to connect to the Inbound HTTPS component is displayed at the bottom of the configuration screen (Test and Production).
- It can only contain letters, numbers and these special characters:
@._+~?. - It must be between 3 and 50 characters long.
- It has to be unique within a tenant.
Use the 'Validate Endpoint' button to to ensure the URL is unique within your tenant.
The maximum body size of requests to an Inbound HTTPS component is 10MB.
Tenant part
Specify wether the tenant name or ID is included in the URL.
Options
Tenant name(default)Tenant ID
Match prefix?
Specify whether the endpoint URL should act as a prefix, enabling one Inbound HTTPS component to 'listen' to multiple incoming URLs.
Options
YesNo(default)
The default No, only allows the exact URL that the component generates for inbound requests. For instance, an Inbound HTTPS component with the Endpoint myflow can only be reached at:
https://[instance].dovetail.world/inbound_https/[environment]/[tenant_part]/myflow
Set the Match prefix to Yes if you want the component to also handle URLs as shown below. Now myflow is the prefix for inbound requests, allowing the Inbound HTTPS component to handle messages sent to different URLs.
https://[instance].dovetail.world/inbound_https/[environment]/[tenant_part]/myflow/user
https://[instance].dovetail.world/inbound_https/[environment]/[tenant_part]/myflow/order/1
You can retrieve the full URL or the partial URI of an inbound request from the CamelHttpUrl or CamelHttpUri header respectively. They are available when the Preserve HTTP Headers option is set to Yes.
Preserve HTTP headers
Specifiy whether to retain the Camel HTTP headers on the incoming message or to remove them.
Options
YesNo(default)
Exchange pattern
This option determines how the Inbound HTTPS component responds to incoming messages.
Options
One wayRequest reply(default)
Request reply
When set to Request reply, the Inbound HTTPS component responds to an incoming request with the result of the flow, even if the flow's Transport Type is Asynchronous.
The response is the message (body and headers) at the end of the flow. Alternatively, the response is the message before reaching the first component whose 'Exchange pattern' is set to One way.
If the Exchange pattern of the Content Router in the image below is set to Request reply the Inbound HTTPS component will respond with the message state at point 2 (top or bottom, depending on how it is routed). If the Content Router is set to One way, it will respond with the message state at point 3.
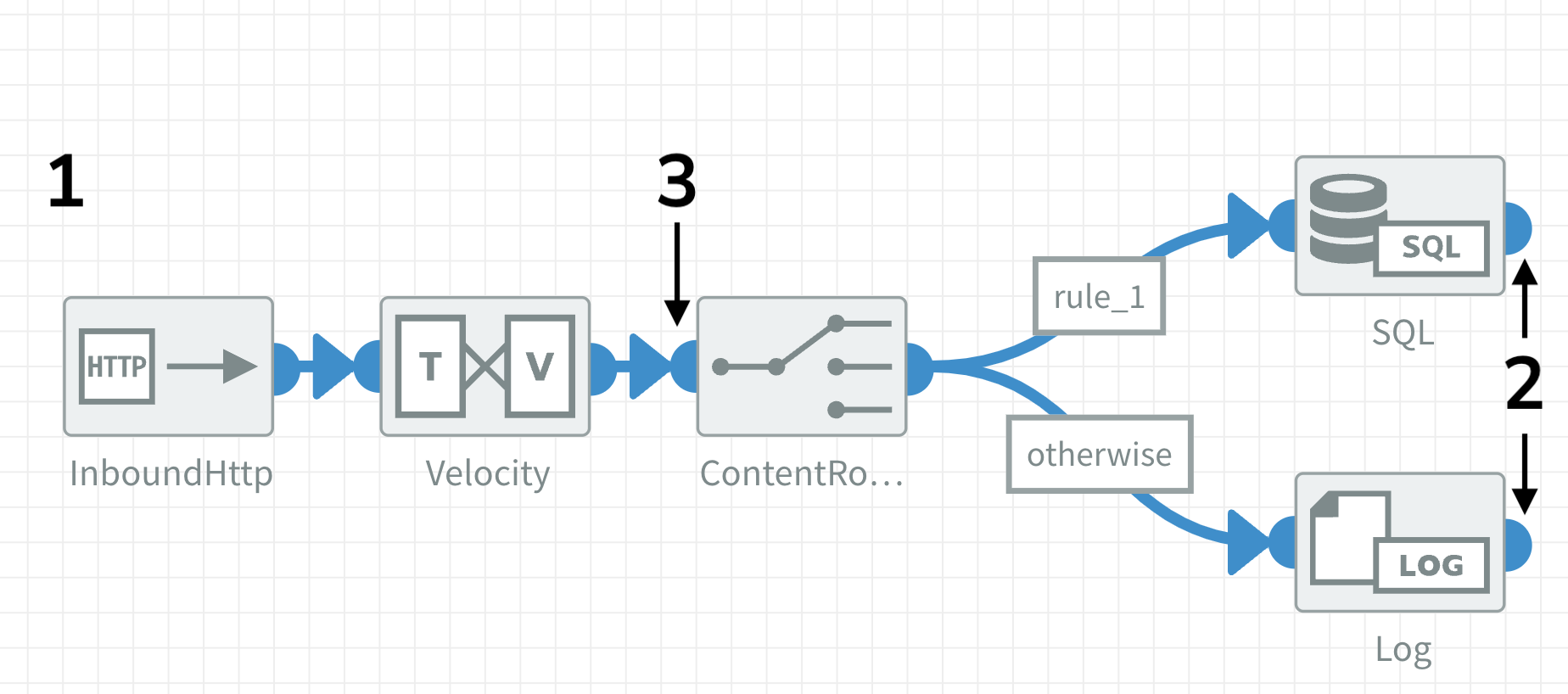
The Components Timeout setting of a flow may need to be increased when using Request reply to allow enough time for processing incoming requests.
If an Inbound HTTPS component responds to a request with a 500 error, it often indicates oversized headers in the response message rather than server downtime.
Use a RemoveHeaders component before the point where the response is sent back to clean up the headers. In the image above: after the SQL / Log or before the Content Router component.
One way
Sometimes you don't need the result of a flow as a response. Or, for large or complex flows, processing can take too much time for the Inbound HTTPS component to send back a result. Some clients will wait for a response, but others may time out.
To immediately return a response after receiving a request, set the Exchange pattern to One way (point 1 in the image above). In this case, the component responds with HTTP status code 200 OK and the body it received. This only works when the flow's Transport Type is set to Asynchronous or Queues.
Using Inbound HTTPS
Default Endpoint
An Inbound HTTPS component with the following settings:
- Endpoint: 'Set flow name as endpoint'
Enabled(flow name:myflow) - Tenant part: Set to
Tenant name(tenant name:mytentant)
https://[instance].dovetail.world/inbound_https/[environment]/mytenant/myflow
Manual Endpoint
An Inbound HTTPS component with the following settings:
- Endpoint: 'Set flow name as endpoint'
Disabled(manually defined endpoint:myendpoint) - Tenant part: Set to
Tenant ID
https://[instance].dovetail.world/inbound_https/[environment]/[tenant_id]/myendpoint
Testing Inbound HTTPS
Use a REST client like Postman to send messages to an Inbound HTTPS component in Dovetail. This allows you to manually trigger a flow or to send test data to it. Follow the steps below to send a request with Postman:
- The URL of the Inbound HTTPS fot the environment you are testing
- Set the HTTP method to POST.
- To send an XML or JSON body:
- Click on the Body tab and select Raw message format.
- Paste your XML or JSON in the text area.
- To send headers:
- Click on the Headers tab and add the Key (header name) and Value.
- Click Send to submit the request.
Verify wether the message was recieved succesfully:
- Look for completed (exchanges) in the Flow Manager - Overview
- Look for transactions in the Flow Manager - Transactions
Send a header as a parameter by appending it to the URL. Start with a question mark (?) after the URL and combine multiple parameters with an ampersand (&). For instance:
../[tenant_part]/[endpoint]?headername=headervalue../[tenant_part]/[endpoint]?headername1=headervalue1&headername2=headervalue2